Notes best practices
These best practices are created as a set of personal choices, based on previous experience (since last millennia, around 1994) with many tools and also how to better extract information from the data stored in my notes. I design things based on how I use them, not the other way around. With that I mean that the tools will adapt to me (most of the time) and not the reverse.
There are some particularities that apply to my use cases only, while many things can be broadly used with the same results or even as the basis for something better. If you happen to see these notes and have any suggestion for improvement, please share it with me.
This is not an exhaustive list nor a complete note: it will be expanded as and when things evolve in my eternal note-taking process. It has already evolved from various systems and is currently being updated to Obsidian terminology.
For basic Obsidian things, please check my other note: Obsidian - getting started.
Main takeouts
- Use standards whenever possible (YAML, JSON, CSV, WikiLinks, ISO-8601, ASCII, etc.).
- Use templates and automation to keep the overhead low.
- All important information and metadata must be part of the note, trusting OS metadata leads to wrong status and answers. (See Managing time and dates in notes / Managing time in notes)
- Design things for how they'll be used, not only for input.
- Backup is not sync, sync is not backup: they serve different purposes and should have different specific strategies.
- Keep add-ons / plugins to a minimum, using them only when the core functionalities do not address an existing real issue (and don't install them based on something that might happen someday).
- If it works for you, it doesn't matter what other people do: keep moving!
- It isn't because it works that there's no better way to do it: test and improve often. (See An example of vault evolution — Template change/ Vault evolution and changes)
- Functionality over appearance — but it can't be ugly.
- What you don't work with, you don't know (take care with Artificial Intelligence, large language models, Machine Learning and automations to generate things).
- The quality of your work while inputting and maintaining your notes is proportional to the quality of the output you get from them.
What about the 'second brain' concept?
This is more specific to Obsidian, as it is touted as a second brain. I don't see it as a second brain, but a note repository. A brain is able to autonomously identify new concepts and create new things and solutions. It can change and optimize relationships and contents.
Obsidian allows for improvement on a person's single brain by helping recover concepts, analyze relationships between them, identifying common topics, etc. but it does not produce any new output per se. Some plugins related to Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence allow for some of that, but they are not Obsidian: they are services that are integrated into Obsidian via plugins. AI can be used for note processing with Obsidian, but the gains to the person itself aren't clear if everything is automated (I mean: you end up with a note repository, where some of these were created or manipulated by an AI, but you still will use it by searching what is in there).
Folders
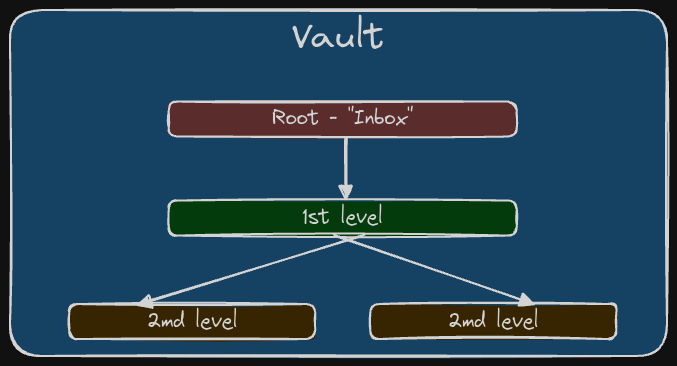
With a single repository, a first level of categorization is desirable. Using folders as a first categorization level requires them to be broad, and Tiago Forte's PARA Method provides a first start for that. I've been using something similar to it for decades (yes, from before PARA existed) and it works well inside Obsidian and outside of Obsidian, including scripting tools, file explorers, email clients, etc. Having a single and consistent method to organize your information will make finding and associating that information between tools easier. See Connecting information and notes / Connecting information and notes.
With time, and through the years, the structure changed and nowadays in all my tools I ended up with something similar to the example below.
- Articles
- Published
- Assets
- Home
- Car
- Stocks
- Body - Mind - Soul
- Cooking
- Health
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Excalidraw
- Libraries
- Palettes
- Pens
- Scripts
- Templates
- Family
- Myself
- Wife
- Son1
- Son2
- Travel
- (common interests and activities)
- Glossary
- Journal
- (Year-Quarter)
- Weekly
- Yearly
- Kindle
- Management
- Finance
- Knowledge
- Leadership
- People
- Projects
- Stakeholders
- Resources
- Dashboards
- Omnivore
- RegressionTests
- SuperTags
- Templates
- javascript
- webclips
- Study
- (languages)
- (other self learning contexts)
- MBA - Strategic Enterprise Management
- Work
If the order in which these are shown is significant, it is wise to count on the name of the folder and an alphabetical sorting: 0-9, A-Z, a-z, '-' (using spaces is fine on modern systems, but it will often require additional operations to process it, so it is recommended that it be avoided). Some note systems – such as Evernote – allows for special symbols (“@”, “!”, etc.) to be used. Remember that these might not be 100% portable, so if future-proof is a concern, keep the names within the ASCII (ASCII - Wikipedia) letters and digits limits.
Note that, in the example above considering some Obsidian plugins, if the system requires folders for itself, they should be created considering the defined folder hierarchy. Sometimes it is easier to create them as top level folders, other times as subfolders… If you are unsure that everything supports subfolders, opt for consistency and use top level folders for all system tools. Things can be migrated as time allows for it, so the above shows some plugins with folders at root level, while other plugins have their folders as a subfolder from Resources folder simulating a migration in progress.
The folder hierarchy should be as shallow as possible. They are only relevant for a first categorization of your notes and most of the structure will be repeated inside the note: for everything that you want to save, you should make it part of the contents of your notes. This should be done as metadata, either at the #YAML / Front matter / Properties (Obsidian) or at the note body.
Also note that if there are folders too specific per subject, friction will be created on the “where to save this information” decision-making process.
In my experience, to address this issue of “where to save this”, think on what made you create that piece of information or what led you to it. Use that as the decision information and group things together this way. A good searching tool will find it, and you will always remember why you have the information in your repository when you see it.
Attachments
I use the option of having my attachments in separate folders. And, for the folder, I ask Obsidian to create a folder one level below the one I'm writing the note in.
This helps to group information and, if I need it one day, everything related to a particular set of notes is available together. This can be used for exporting data, sharing data, processing data… all the information is complete.
I name that folder as 00attachments to have it show up in the folder hierarchy. If I wanted to show it as the last folder, I could prefix it with zz instead of 00.
- Assets
- Home
- 00attachments
- Car
- 00attachments
- Stocks
- Excalidraw
- Palettes
- Pens
- Scripts
- Family
- Myself
- 00attachments
- Wife
- 00attachments
- Son1
- 00attachments
- Son2
- 00attachments
- Glossary
- Journal
- 2021-Q1
- 00attachments
- Weekly
(…)
To enable that, I have the highlighted settings configured in my Obsidian:
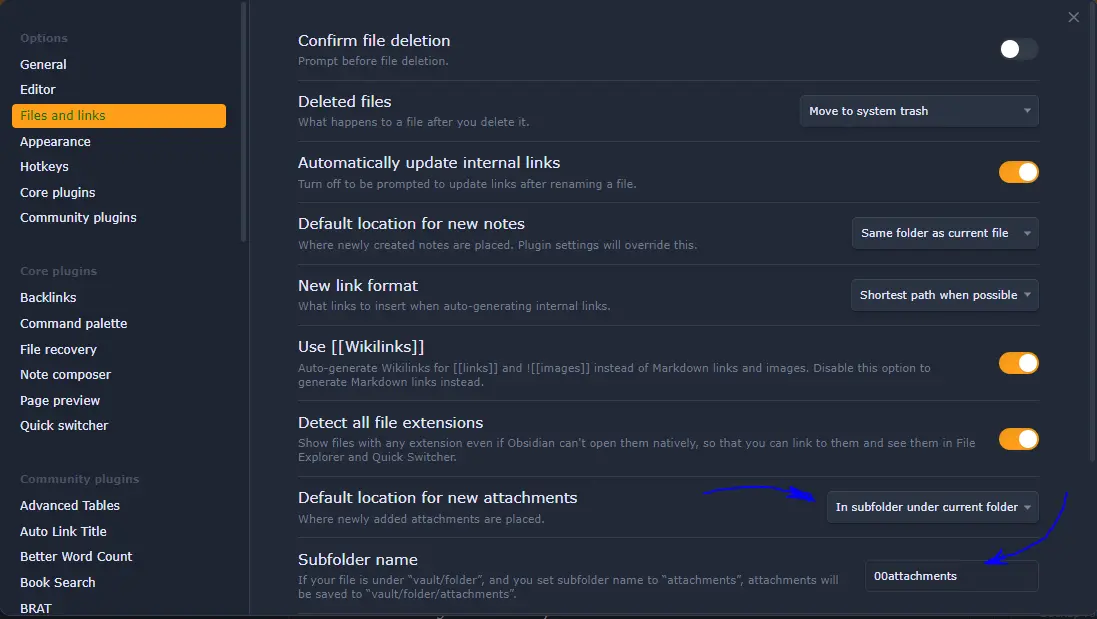
See How I handle attachments to my notes in Obsidian for some extra information.
Plugins (Obsidian), extensions, modules, add-ons, etc.
Use as many as required, no more and no less. If you end up some time without using a plugin, consider disabling it.
Be strict with what is needed and with how it might impact the note-taking workflow and data consumption in case the add-on stopped being maintained or disappeared.
It is interesting to test and try what add-ons can do and document how to use them hastily (#Testing and Regression tests).
As a bonus tip, for add-ons that are constantly used, it is nice to have templates on how to use them, reducing the time and need to copy and paste from other examples.
Always search for how to add comments on the template code, so that you can use it as a personal documentation of the add-on.
Templates
Some common useful note templates to think about and have set up:
- Meeting minutes template — a generic meeting template that applies to meetings in general.
- Book notes template — for when I use the book search plugin.
- Projects template — a generic project template (that I ended up not using that much…).
- Journal template — for may daily note, that includes; my journal; some health, and fitness metrics; an overview of what is planned for that day.
- Template - WeeklyNote — for my weekly planning that will be included in my daily journal note.
- Generic template — so that some automation on metadata can be applied to all notes in the repository.
- Glossary template — a template for glossaries and definitions.
- Stakeholder template — standard items I track for companies and people (my simple and personal “CRM”).
There are, also, templates for the contents of notes, not just the initial note itself:
- Individual meetings - Occurrence
- Feedback meetings - Occurrence
- add-ons templates (charts, images, etc.)
And, since templates allow including other templates, this also simplifies standardizing things. I have templates for:
- Template - Frontmatter - Dates — to standardize the date fields / properties I have on all notes.
- Template - NesteDiaToday — to automate the code to show everything that happened on that day, even in past or future years.
- Meeting headers, etc.
Since the folder layout defines a higher level classification, it can also be used to specify which template notes created within that folder (and possible subfolders) should use. It is a nice setting that must be explored whenever possible. I expanded this to using regular expressions as rules. Even with folders as patterns, this makes it easier to create possible exceptions or to adapt it to folderless scenarios.
Using the folder layout presented earlier, and the existence of a Journal template, this template could be applied to all new notes created within the Journal folder, speeding up the process. It is also possible to have a template for one folder and another for a folder one (or more) level(s) below that. For example, a daily template at the Journal folder and a weekly template at the Journal/Weekly subfolder.
When the system does not allow for using templates, then having the same folder with contents that can be inserted into a new note – or copied to a new note – will help with consistency. For some systems, this is how template worked for many years (ain't I right, Evernote?) and it is a good solution to avoid repetitive typing and possible spelling errors or typing errors (“typos”). It is recommended that these special notes start with some characters that either place them at the beginning or end of the list, so that they don't interfere with the reading flow (some examples of such characters that are also compliant with the other recommendations above: 00, 99, zz, etc.).
Note contents
Dates
The last line of the #Folders section talks about everything that should become part of the note. This is valid for hierarchies, folders, note title, etc. and it is very important for dates.
Counting on a single Operating System (OS) ability to keep date and time information is something that often comes up with surprises… When you get more OSes and devices in the mix, things get even more complicated and surprises come up more often.
It is better to rely on the note contents – and possibly automate that – than to rely on multiple OSes respecting each other's rules in different devices: more often than not, one device does not know the other device exists.
Planning for date usage / date filtering
Take into account the best practices documented by the BI community: processing a huge amount of data with date-related dependencies is their day to day, so why reinventing the wheel?
When it is possible to choose date and time formats, ISO-8601 (ISO - ISO 8601 — Date and time format) should be used. It will help with automating things (as all programming languages support that standard) and even sorting file names (the format specifies dates as YYYY-MM-DD format, which is sortable by default).
The following fields – and formats as per ISO-8601 (and a particular moment.js case) – are recommended to exist on all notes (add them to the note templates and let the system fill the data on your behalf):
| Field | ISO-8601 code | Example output | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| created | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss | 2023-01-02T07:08:49 | file creation date and time |
| modified | YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss | 2023-05-02T07:16:46 | file modification date and time |
| date | YYYY-MM-DD | 2022-03-22 | file creation date |
| week | ww | 12 | file creation week of the year |
| weekday | dddd | Sunday | file creation day of the week |
| weekyear | gggg-[W]ww (see [1]) | 2022-12 | week of the year, including the year |
| month | MM | 01 | file creation month of the year |
| monthyear | YYYY-MM | 2025-01 | month and year together |
| quarter | [Q]Q | Q3 | file creartion quarter of the year |
| quarteryear | YYYY-[Q]Q | 2025-Q2 | quarter and year together |
| year | YYYY | 2005 | file creation year |
For Obsidian, you can use the following code with Templater plugin and considering that the note is being created 'now':
created and modified are added automatically by the Obsidian Linter plugin (GitHub - platers/obsidian-linter), with modified automatically updated after every manual save of the file. Linter has since been upgraded to lint files automatically.
tp.date.now can be replaced with tp.file.creation_date, for example: date: <% tp.file.creation_date("YYYY-MM-DD") %>
It also accepts a reference to generate the date in the format of (my journals have the date as the title in YYYY-MM-DD format): date: <% tp.date.now("YYYY-MM-DD", 0, tp.file.title, "YYYY-MM-DD") %> .
Lately, I've improved this further to use moment.js with the following codes as examples for new syntaxes in use: moment(tp.file.creation_date("YYYY-MM-DD"));, moment() and moment().format("YYYY-MM-DD").
Even if many of these can be derived from the created field, it is recommended that all of them are part of the note (or its metadata / properties) for filtering, searching and grouping purposes. It adds very little to the note size, but will save time and make queries less complex in the future.
Changes can be made to the above recommendations, but you should consider how you'll post-process the notes in the future (if you will post-process them at all). This includes looking for trends such as productivity every month, information in other metadata fields per quarter, etc. The order is not important as long as the values are correct and can be found via, e.g., a search (this is the most basic test to everything, see #Testing and Regression tests).
I've written more about dates in notes in my note Managing time and date in notes / Managing time in notes.
Times
There are cases where processing time is critical, especially processing durations. For that, I also use ISO-8601.
Examples where I use these are for tracking exercise time, intermittent fasting duration and my sleep levels. Below there are some example entries, with inline Dataview fields.
- LightSleep:: PT03H31M
- DeepSleep:: PT05H56M
- Cetosis:: PT18H12M
- Fasting:: PT30H12M
- ExerciseTime:: PT56M
Linking
Links, in Obsidian, should be written as much as possible as WikiLinks with double brackets [[link]]. These are updated automatically when the name of the destination file they link to changes.
For URIs (Uniform Resource Identifier – this is the father of URLs) the standard Markdown link format should be used: [visible part](link target).
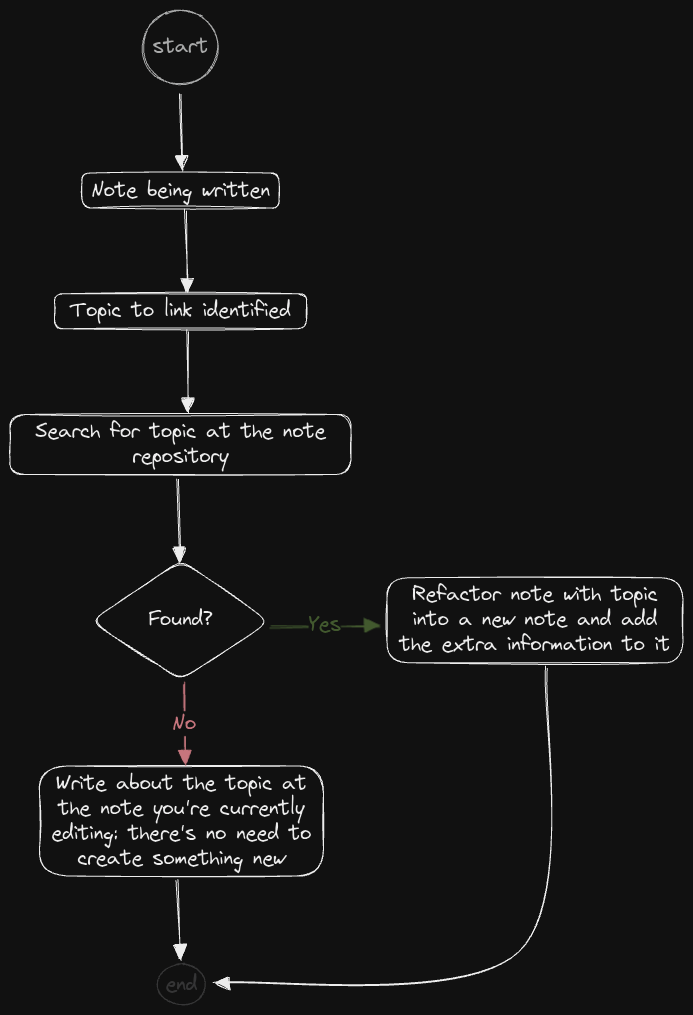
Finding notes to link to
There are plugins in Obsidian that help with that. The core backlinks plugin is good to check for missing connections. There are more 'proactive' plugins – such as the Various Complements plugin – that make suggestions as one person is typing the current note. I've gone with the core plugin for now… But if required, using an additional plugin to obtain more insights from my notes is not something I'd avoid.
A good thing is that when a topic shows up, if you don't know if it is already covered in your repository or not, then you can easily search for it. Use different keywords for the topic, just in case you missed some alias or used a different title.
If you find the note with that topic, or a note discussing it, then link to it (if in another note, you might want to refactor that into a new note for the topic alone…). If you don't find one, then create a link and once the current note is finished, then go back and – if it is a good time for that – create the new note.
Detailing the process:
Front matter vs. note body
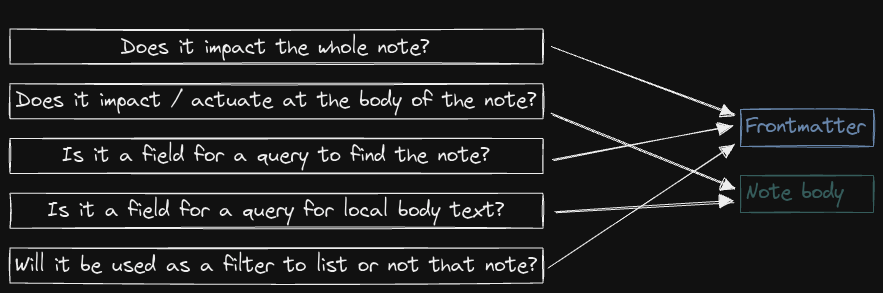
Simple of example of decision process for where to add metadata information
Anything on the front matter refers to the whole note. If the information is valid for the note, it should be added there.
Anything on the body note refers to that specific part of the note.
Context dictates where things go.
This is valid for data fields, variables, block IDs, tags, etc.
On the tags issue, particularly, those are global per nature, but some plugins — such as Tasks and Dataview plugins — use tags to find items in lists or task lists.
Tracking contacts information
As a user of Android and Gmail for a long time, I have all my contacts sync'ed with Google Contacts.
For people, and some vendors, I have a contact with their full name and a note with the same name (full name), having a “Contact information” section at the note linking to the Google Contacts site. The same can be done from the contact site, with a link to the note with their name – but I didn't get to do it out of laziness. It can use the “obsidian://” URL targeting the note.
I've generalized this and created a Template - stakeholder template file.
I don't have a note for every contact. Some of them are only linked to a note that doesn't exist. If the need arises, then the note is created. As contacts are already linked, once these notes are created they will work for all existing links. For links that do not exist, the Backlinks core plugin helps to find these items.
Also, nicknames, abbreviations, etc. that are commonly used should be listed as aliases, allowing the recognition and automatic suggestion of those values as well.
Mathematics
When possible, never hesitate on using
If it is not possible and the system do not offer something usable (Equation editor, I still remember you!), then draw it with
Note length
A note should be as short or as long as it needs to be. There's no need to optimize early.
If a part of a note is required in multiple other notes, then refactoring can be done.
The exception to that rule is for items that are already known to be reused often, these should be created as separate notes right away.
If unsure, let it all in a single note until refactoring / reuse is required.
This has further evolved in Splitting Notes.
From here, you can end up with Atomic notes and Molecular notes.
Multiple languages
As a person who speaks, reads and talks more than one – or two – languages on a daily basis, I have notes in mixed languages. You might have already noticed that here.**
The easiest way to cope with that is writing the note in the language that suits it better – be it audience, usage, based on the language of the source, etc. Then, having multiple aliases covering all the languages where the note might be used will take care of linking even if the note is cited in a different language. Today, translation services can be automated, so there's no reason not to write in the language you want to.
For example: personal notes might not require a second language, as they are usually written in your mother tongue; but work related notes can be in multiple languages, and the same applies for notes to be shared with the Internet (such as this one).
The other alternative is using a single language for everything, but then be careful with automation sources and information generated by #Plugins (Obsidian), extensions, modules, add-ons, etc. as they might come in a different language, making the text out of place.
Note structure and contents evolution through time
Making changes when there are many (hundreds, thousands) of notes in your repository is always hard.
The more structural the change, the harder it gets. (Metadata, I'm looking at you! Header structure / depth, etc.)
Some note-taking applications allow you to make mass change to notes with the application itself, while others either don't allow mass change at all or allow it only through external tools.
Use what is better. Remember to backup first (#Backup vs Sync).
The important thing is: you will change with time and as you know the tool better, so don't fear changes. Think on how to implement them, try some kind of automation, take a deep breath and go for it. Sometimes you might want to process all notes at once. Sometimes you might want to make the change valid from that moment forward, ignoring old notes.
It will depend on what the tool allows, how you will use the new structure, and how willing you are with partial results until everything is migrated. If you have a kind of archive for old reports / automation, don't worry and use it. At last, you can also adapt the automation to work with both scenarios, in case you keep old notes without the upgrade or until the upgrade is complete.
Check Vault evolution and changes for an example.
Note relationship
I usually don't specify any special relationship between notes, but I'm willing to experiment improving how things are related to each other.
For that, my option of choice has been using a cardinal representation of these relations:
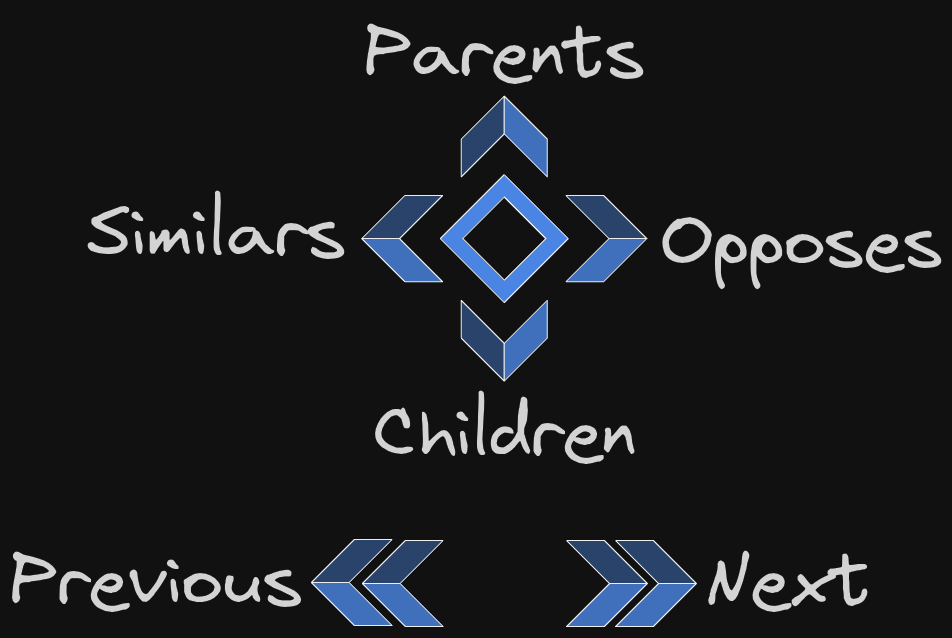
The cardinal representation comes from note properties with the names above, in lowercase: parents, children, similars, opposes.
The “previous” and “next” relationship is the currently obtained with links (next) and backlinks (previous). But, I also have them as part of my possible properties, just in case I need that reference somehow.
The exhibition of that relationship graphically is — here at my vault — performed via the Excalibrain plugin (GitHub - zsviczian/excalibrain: A graph view to navigate your Obsidian vault).
This kind of assessment makes analyzing notes relationships a bit more complicated, but this also might lead to more insights and a better understanding of the information with richer contexts and more complete ideas.
You can find a lot more of contexts at Semantic linking.
Backup vs Sync
There are two concepts that sometimes get misinterpreted. Note repository (or individual note) synchronization (sync) and backup.
The idea for a backup is taking a snapshot of the note or the note repository at a given moment in time. At the moment of the backup, the backed up objects must be in a healthy state, so that it can be recovered with little to no effort in case something goes wrong. It is also important to know that if the "backup" is on the same computer disk as the original files, then it is not a backup. The backup must live in a different media (an external SSD disk, for example).
On the other hand, the purpose of synchronization is to maintain two or more copies of the data equal. Replication can happen in one or two directions: 1) from the user to the repository; or 2) from the user to the repository and the repository to the user. The most common implementations available to users consider that replication can happen in both directions. This has been popularized with cloud solutions and the need to sync things between computers and mobile devices, where changes can happen in both devices.
There are peer-to-peer alternatives for replication that do not go through public clouds. One of them is syncthing, which connects authorized devices when they are available in the network and sync their data in both directions.
It is also possible that some solutions can work with both scenarios, and this is what usually happens with code versioning systems (CVS) such as git, Subversion, etc.
Considering portability and easy of setup, git with GitHub (now that personal repositories can be private and free) is a very common alternative to end users.
Backup routine
Nonetheless, even though git – for example – can make both roles, it is good to have offline backups or have them stored in a different cloud other than GitHub's.
A good backup schedule depends on how risk averse you are. The more averse to risk, the closer your backup windows must be. For non-critical data, a weekly or monthly schedule is fine. For critical data, you might want daily backups at least.
Sync
With Obsidian, my strategy for sync has moved to OneDrive. This allows me to benefit from some desirable side effects:
- OCR and indexing of images and PDFs.
- A simple version history for files.
- A 1 TB storage area for the vault and companion files (images, videos, audio, PDFs, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, etc.).
- Integration with Microsoft Copilot. (It is important to check for possible privacy issues here!)
Dashboards
I use dashboards as central consolidation panels. I have them for:
- birthdays and anniversaries.
- books read.
- recently changed and created notes.
- existing note categories and types.
- health tracking.
- inexistent notes and untitled notes.
- TOP 5: tags, categories, biggest files, referenced files (inlinks).
Every item above is a "module" and can be embedded to a note to show its results and create a "control center" or "visualization center" for everything.
Particularities
Books
Here I use the Minimal Themes cards view to present book covers and some data. Initially I only had what Kindle Highlights plugin provided. I've later expanded this to also allow for Book Search plugin results, where I planned both possibilities to generate a similar structure for the highlights.
Health
For health tracking, I use Obsidian Charts plugin. One thing that bothered me for a long time - until I was enlightened - was plotting the duration.
I had an issue with the Y-axis with the duration overflowing every 24h and restarting from midnight when the duration was longer than 24h.
I have solved this with the conversion of the duration time to decimal hours, with a function native to moment.js:
var fasting = pages3.map(p => Duration.fromISO(p.fasting).as('hours')).values
var cetosis = pages3.map(p => Duration.fromISO(p.cetosis).as('hours')).values
With that, Y-axis becomes a numeric axis and plotting any value becomes simple.
X-axis contains the date of the measurement.
Testing and Regression tests
These are simple use cases that can be thought of as a check on upgrades to see if anything fundamental to the daily workflow is broken or not.
It also serves as additional documentation for add-ons and features used in the note repository.
Make these simple, and then complex: a minimum of a simple implementation and a maximum of two or three implementations on the same note. It won't matter if there are 50 use cases in your repository if the simplest one stops working or if a critical complex implementation stops working.
The RegressionTests folders also serves as a playground for testing new add-ons without polluting the rest of the repository. This test will become part of the regression tests you'll have in case you decide on maintaining the add-on in your repository.
When implementing new contents and automations that change the notes themselves, one of the basic tests that can be performed is a simple search text on the new string as well as on the old string.
Final note: a Jack of all trades?
Is Obsidian – or any other tool and especially note-taking tools – the ultimate solution to all problems? Unfortunately no.
There are lots of specialized tools that perform much better than Obsidian.
What we should seek is:
- Reducing the number of tools for everyday tasks
- Using the best tools for what needs being done
- Trying to integrate all the tools we have
For example, it is easy to create a semi-CRM tool with a note-taking app such as Obsidian, but then other apps that use the contact information will lose their ability for that (WhatsApp, Telegram, Twitter, etc.).
The best option is linking to those tools so that when the link is clicked you get access to the information or duplicating the minimum possible information, while also keeping a link to the information at an app or website.
Related Notes
ggggis a moment.js implementation due to the year obtained with YYYY changing, even though the week still belongs to the previous year in cases where we have 53 weeks in the year. Other systems might have a different meaning for thisGGGGformat or have a different implementation to consider the same limitations addressed here. ↩︎